Hosted on 10 of August 2022
This report is in reference to a one-day workshop organized on August 10, 2022 at Lower Motowoh Community Limbe. The workshop was organized by Dreamer’s Hope Foundation. The objective of the workshop was to foster peace in our communities there by identify the role of communication, trauma, teamwork in conflict as well as causes and effect of conflict management in our communities and possible solution. On the others hand building an eco-friendly community. This workshop was attended by 20 participants made up of Women, Men and Youths Respectively.
The workshop was facilitated by Ms. Beltha Asek, Project Coordinator, Ms. Desse, and Shafe Bertrand who were the resource persons of the organization.
The workshop began at about 2pm with the arrival and welcoming of participant, followed by Ms. Beltha who gave a brief introduction of herself and the team. She went further to set ground rules with participants as well as their expectations for the workshop. She proceeded on the objectives for the workshop and what it seeks to achieve, Introduction of Dreamer Hope Foundation which lasted for about 10mins. Below is the agenda for the workshop program:
The first presentation was conducted by Shaffe Bertrand on definition of key Concept and definition of conflict Management. Participant were asked to define and give their own contributions to what they understood by conflict management; they defined conflict as disagreement between 2 persons and management the ability to control a thing. Bertrand redefined conflict management as the process of dealing with incompatibility. He went further to explain the various stages to talk on the various stages and style of conflict management.
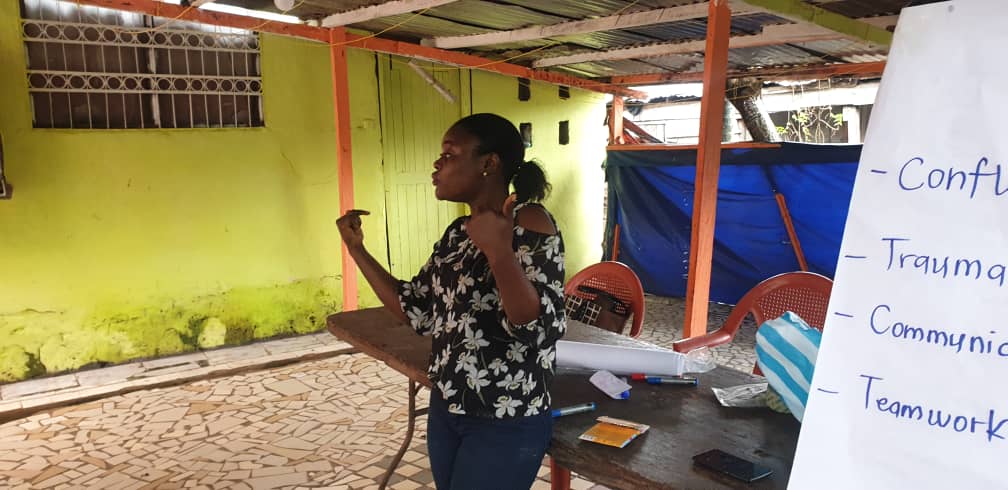
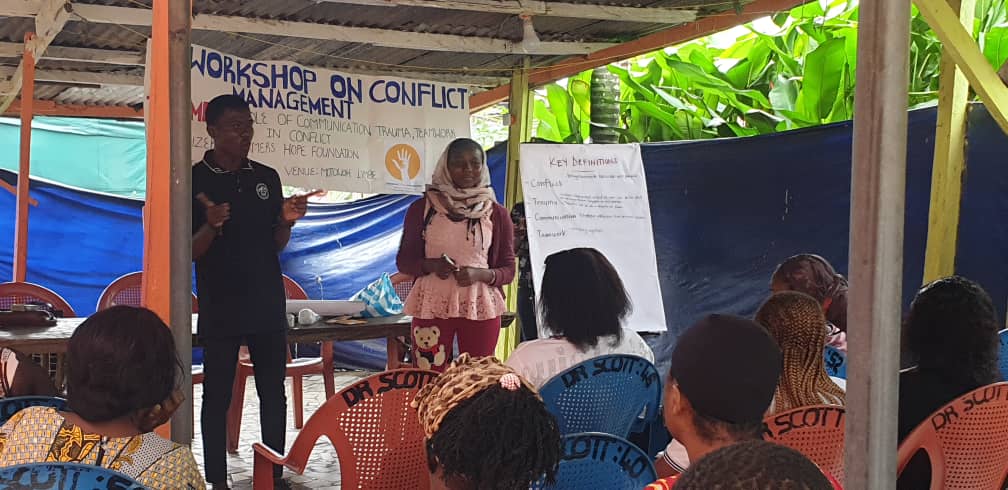


The second presentation was focus on the different conflict management styles. This presentation was facilitation facilitated by Ms. Desse. Participants were asked to verbally explain how conflict can be managed; this was done in other to get participant engaged. The facilitator went further to list outs some of the different styles to conflict management as accommodation, avoiding, compromising, and collaboration, relating it to real life examples. This was done to educate participant on simple techniques to manage conflict locally and other wise.
The next presentation was centered on the Role of Trauma, Communication and Team work in Conflict and Conflict Management. For a more explicit explanation 6 participants were called out to volunteer. They were shared into a group of three. Group one was asked to act out how communication causes conflict in their meeting groups and how it is used to solve. Group three acted on the role of trauma in conflict at home and at school. Participant had to demonstrate different scenario on how these three aspects play in conflict and conflict management and also how they contribute in conflict and conflict management. The presentation ended with participant making contribution and sharing experiences on how these three aspects have played out in their meeting groups, community and workplace.
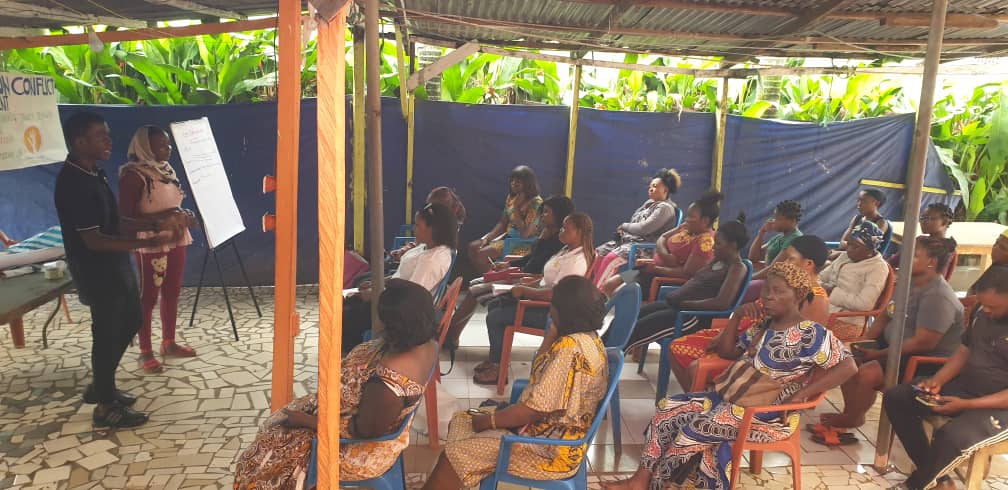
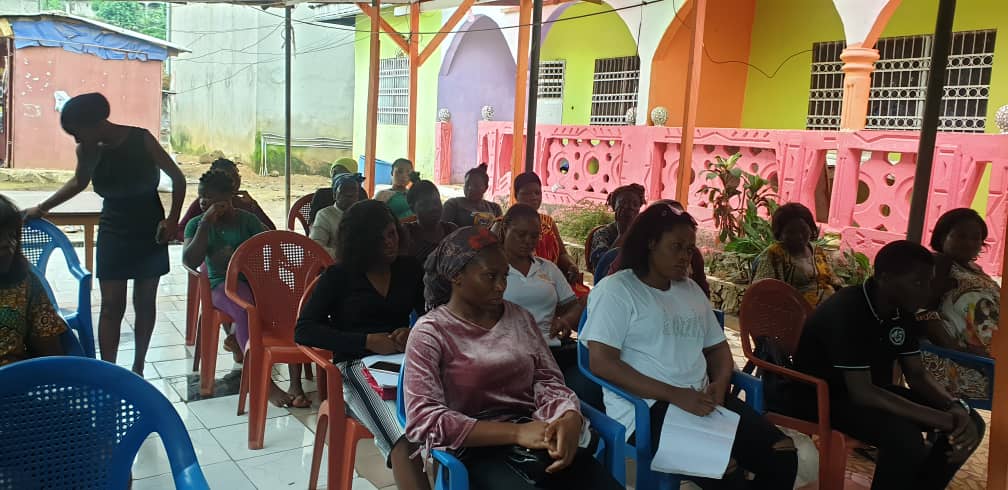


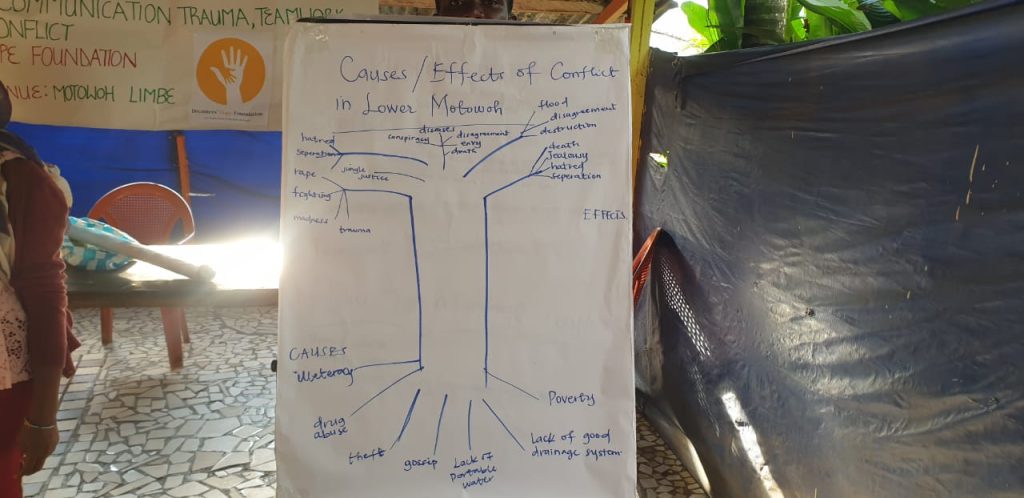
The last presentation was to identify some of the causes, effect and solution to conflict and conflict management in lower motowoh using the problem and solution tree. Participants were asked to list out the problems starting their root causes and possible effects some of the identified causes of conflict were Poverty which leads to disagreements, corruption, jealousy, hatred among others. Other identified causes were illiteracy, drug abuse; gossip leads to loss of lives, fighting, rape, trauma, conflicts among other. Proposed solutions to the above listed problems were; conduct more educative and sensitization programs to crop illiteracy, encourage NGO’s to carryout economic empowerment programs in the community to help individuals to be financially sustained, encourage community involvement in team

The workshop ended at about 5pm with a group picture and departure of participants

Annex 1: Detail Presentation
Topic: The role of communication, team work and trauma in conflict.
Conflict is a disagreement between two or more parties or people in which one person is trying to restrict the interest of another and so when this happens, it leads to fear anger and frustration which later leads to actions and reactions.
Types of conflict
Conflict management
Conflict management is the practice of being able to identify and handle conflict sensibly fairly and efficiently. It is the process if dealing with incompatibility or disagreement arising from diverging.
Latent Stage: Participants not yet aware of conflict.
Perceived Stage: Participants aware a conflict exists.
Felt Stage: Stress and anxiety.
Manifest: Conflict is open and can be observed.
Aftermath: Outcome of conflict, resolution or dissolution.
The various conflict management styles
The role of communication team work and trauma in conflict.
Communication
The imparting or exchanging of information by speaking, writing, or using some other medium.
Teamwork is the collaborative effort of a group to achieve a common goal or to complete a task in the most effective and efficient way. This concept is seen within the greater framework of a team, which is a group of interdependent individuals who work together towards a common goal.
Trauma is an emotional response to a terrible event like an accident, rape, or natural disaster. Immediately after the event, shock and denial are typical. Longer term reactions include unpredictable emotions, flashbacks, strained relationships, and even physical symptoms like headaches or nausea.
How communication causes conflict.
_ Misunderstanding
_ A gap in communication
_ Change in communication
_Misinterpretation
Role team work in causing conflict.
Differences in expectations.
Difficulties in addressing issues immediately.
Treatment among group members should be fair and neutral.
Differences in opinions and decisions making.
The role of trauma in causing conflict.
_When someone is confuse with himself.
_When someone cannot be in peace with himself.
How communication, team work and trauma can manage conflict.
When a conflict arises among your team members, action should be taken quickly to resolve it. Instead of ignoring or avoiding conflict, accept it and work towards addressing it immediately.
. Set clear expectations.
Managing expectations – both in terms of what you expect from others and what they expect of you – is one of the most important things a team can do to facilitate better communication. Anything you or your colleagues need from each other should be clearly
. Build active listening skills.
You may be hearing what your colleagues have to say, but are you actually listening to them? People’s minds often wander when others are speaking, especially in a group setting, and they don’t truly absorb what’s been said. Even in digital communications, it’s easy to read a message and immediately forget about it. Gamlem emphasized the importance of creating a culture where people
Use neutral terms and open body language.
When engaged in a conflict, it is natural to want to be closed off – but this only hinders the chance of resolution. Give yourself (or those in the conflict) time to cool off first. When managing the conflict, speak in a calm, agreeable manner.
Use neutral language and separate the other person from the problem. It is better to speak in “I” language, as opposed to “you” language to avoid the other person feeling attacked. For example, saying “I feel undervalued in my position” is going to be more effective than saying. “You don’t value my work.” Using “you” language will only cause the other person to get defensive, which doesn’t bode well for conflict resolution.
Effects of conflict.
Illness.
Copyright – 2019 – Dreamers Hope Foundation- All rights reserved. With love form Djemtech.